|
I used to not know. I figured a lot of top coaches ran back-to-back appointments 12-16 hours in a row, or logged 7 day weeks all the time. When I was at Bally’s 2004 to 2010, I had a peer who once did 141 sessions in a pay period, beating my personal record of 113 (65 in one week and 48 in the other) by quite a bit. These are only the 60-minute sessions, mind you. To those hours add notes, prep, scheduling, consults, assessments, meetings, workshops for CECs, etc. When I was at Lifetime 2010 to 2012, I once had a peer who about matched my record $65k productivity in a month, and several who beat me in the quarter. This was a lot of sales, but also a lot of serviced appointments. Granted, I was managing as well. But I just figured this is how workers work. My performances stood out. My teams did set a lot of national records. But they weren’t wildly divergent from other top performers. And frankly, people had bested me lots of times at lots of junctures along the way, in a month or a week or a quarter. I didn’t see these outcomes as spectacularly unique. There are many amazing pros out there in the top one-tenth of one percent.
Then, as I ran my own business in the independent sphere, often outstripping these hours and performances, I began to realize something was a little bit different about me in 2013. At the large facilities and giant corporate companies, I maybe stood AMONG the top one-tenth of one percent. But in the independent sphere, I found not a single person running the sheer number of client appointments that I ran, week after week, year after year. No one in all of the fitness influencer or strength-coaching sphere has ever shared calendar screen captures like mine. No one. Not ever. Not close. Not by miles. For about a year or so, I would post my wake times and a message on Instagram, somewhere between 2:15am and 440ish, depending on the day. Scroll way back on my Instagram and you’ll see. But still, I found no one sharing schedules like mine. Wake times, sure. But no calendars like mine. No one. Ever. And it started to dawn on me that no one has ever even been close to the experience I’ve logged in strength coaching and training. No one. It’s not a brag. It’s just that no one else on earth is built to be able to focus on others up to 18 hours in a day without breaks, and do it for decades. No one. It’s possible there are some guys in their 70s who’ve coached or mentored as many hours as I have. But again, only I have the receipts. Plus, everyone knows how consolidated intensives simply produce more learning. A person who practices piano for six hour per day every day for five years (about 10,000 hours) is simply going to be better than a person who practices one hour every other day for sixty years (about 10,000 hours as well). I just haven’t seen one person ever share even a short season of busyness that compares to my standard week of two decades. I have some great peers. I admire some great personalities who have curated vast social media followings. But respectfully, none of them are even close to the experience I’ve logged. I love ‘em. God bless ‘em. But humbly, I am the pinnacle in this domain. Not at everything, mind you. But at quite a bit in human performance, actually. This is not an opinion of conceit. It is an objective measurable fact. We could look at my own metabolic experiments or client testimonies. However, lots of coaches have gained 80lbs of muscle and lost 70lbs of fat personally while having trained dozens of people through 50-200lb transformations. That isn’t very unique, actually. I could make a very lengthy list about bringing one of my clients to be an IFBB pro bodybuilder in her 60s, a client who lost 140lbs in 8 months, clients without limbs, clients without sight, clients with cancer, clients whose outcomes that absolutely boggle the mind, and some with 10 to 20+ year success and progress. But somewhere out there, you are still going to find a handful of coaches with a cool story for each of mine. I do doubt you'll find it all in one other person. And I am confident it's totally singular to have been doing that without a lull for two decades. Moreover, I’ve done that AND I have seen my kids nearly every day of their lives, I have kept my friendships, my relationships, and really just a fairly low-profile and balanced (as of the past 6 years) life. My wife has been urging me to create workshops for men who want to be top performers and energy dynamos, and for trainers and coaches who want to be at the top of their abilities. Part of it is because I have now coached several famous influencers. Part of it is because I have coached many clients who previously trained with famous and world-renowned trainers; yet every time their experience with me was superior. Part of it is because I genuinely have been the most overbooked professional in this industry for two decades. And the distance between my experience and that of the best-known names in fitness is not even close. Regularly, I meet with clients who worked with or are themselves world-renowned/famous influencers, clinicians or coaches. Every single time I uncover insights which that expert never dreamed of finding. It isn’t because I’m better or smarter than all of the top gurus in the world. I’m not. It’s simply because I have more experience than all of them. The way I achieved far more troubleshooting experience than every expert in the field of strength coaching and personal training is by consistently booking significantly more hours of appointments than any of them have ever covered, even in the busiest seasons of their lives. It’s just my default. wrote about it ‘19: https://www.elev8wellness.com/wellblog_best_nutrition_training_coaching_experts/experienced-coach-or-good-workout-er And ‘21: https://www.elev8wellness.com/wellblog_best_nutrition_training_coaching_experts/how-to-fit-workouts-in-a-schedule-with-no-time And last year: https://www.elev8wellness.com/wellblog_best_nutrition_training_coaching_experts/5-truths-from-45-hours-of-coaching-in-4-days But also many many times on Instagram and LinkedIn going back to 2015: https://www.instagram.com/p/B1PzPjKDwIp/?igsh=MXVlaGRrMThkdnc4ag== https://www.instagram.com/p/BxN4Nltjzvf/?igsh=MWNkZTcwdDk4czc1Ng== Going back to 2013, all work days were like that. Pick a random Thursday in ‘16; and it turns out I booked 7 hours of sessions on my “off day”. I never found a role model or mentor who even came close. A few guys on social media appeared to put in the sweat equity: Jocko Willink, David Goggins, Gary V, and Dwayne Johnson. But I also noticed they often slept in 1-3 hours later than my usual: https://www.instagram.com/p/BdDAMnznRR3/?igsh=c2Z2cTZlOTQ4NTA5 https://www.elev8wellness.com/wellblog_best_nutrition_training_coaching_experts/there-is-no-kinda-disciplined https://www.instagram.com/p/Bau1khXBUnq/?igsh=amx1bnhsOXJpbXlr https://www.instagram.com/p/BICdWWsDnAE/?igsh=MWc5cW1udzdwcXZi Moreover, they aren’t running packed days like mine focused on other people. Almost all of their waking hours are on self. They aren’t mentoring others thousands of hours per year. They aren’t spending time with their kids every single day of the week. I became my own role model. Most people cannot handle the intensity of 12-16 hours of coaching in a row with no breaks at all. So they don’t. Either they can’t be on their feet that long. Or they cannot mentally focus. They aren’t organized in a manner to keep the notes/memories straight. Business acumen and experience aside, even pretty tough people cannot handle it. So they don’t. It’s not a knock against any of them. They spent their energy and hours on building massive social media followings or on gaining suffixes, writing books, fame, or obsessive self-improvement which leaves little time in the week for anything/anyone else. They hit their personal limit and hire everything else out. But for me, I can. So I do. But HOW I got here may be more instructive for the newer coaches or even for the many, many, many veterans who pretend to be far more successful than you and I both know they actually are. In recent years I’m more discerning, never overtly working more than 3.5 days per week, but easily logging no fewer than 8 appointments on those 3.5 days (yes, I consider 8 coaching sessions a half day), and typically 12-16 on Sundays and Wednesdays both. Occasionally, I cannot keep a Monday or Friday less than that as well. On very rare occasion, my long days are only 10 hours of appointments (but still 2 hours of note prep and research, NOT counting bookkeeping, spreadsheets, and payment management). Ask my coworkers, employees and peers going back 20 years. This is mostly how it’s always been. I still have pages from my planners in 2004-2010 when I’d get up at 3a, take appointments 5,6,7am, management hours 8-2p, lift, director work 4-7, appointments 7p, 8p, home. And I still spent time with my wife. I still did laundry and dishes. I still mowed my lawn. I still went to family gatherings. Somehow. I wouldn’t recommend it. The cost came from my sleep, recovery, health. I could. So I did. But I also found that at the extreme limits it would impair my value. Technically, I could take even more hours, but my capacity to be electric and engaged for each hour is greatly inhibited after much more than 50 appointment hours in a week I’ve come to notice. How am I the most consistently successful strength coach on earth? It’s not marketing dollars or google ad words. In fact, I am probably the worst person on the planet with regard to these. We have previously hired SEO teams and curated social media efforts. For us, they aren’t a fit. No one addicted to screens and social media is my target audience, I’ve learned. Incredibly successful business owners and academics which I tend to coach often don’t even have a social media account. Most of my super wealthy clients do not even have Meta applications on their phones or devices. So an online presence is nice. But for advanced coaching, it’s actually a hindrance by virtue of being such a massive loss of hours and energy spent on people who aren’t ever going to be substantial supporters. This is also how I’ve discovered that the fitness trainers and coaches with massive online followings are mostly frauds. Not all. But most. The people camping out on YouTube for hours a day and viewing your videos at 3am are not serious, not committed to growth or change, and 110% not investors of any kind. Go ahead and slave to get 100 million followers; and I can pretty much guarantee you have no valid real world coaching experience or business knowledge to discuss. Pay a full-time team to optimize your social and website; and I know you haven’t developed anyone, you’ve never managed people, and you have no long-term or serious clients. I’m talking about how I gained real experience to be a real coach in the real world with real people, running a real brick-and-mortar physical storefront. For tips on the online illusion of expertise or success, you will have to go elsewhere. A few weeks ago I met with a client who’d trained at the Olympic training facility and with the founders of MAT. He has had famous coaches. I’m sure all of those experts are impressive in their own right. But I always find areas they’ve missed. These meetings were no different. I uncovered opportunities for this client to reclaim athleticism that other experts hadn’t dreamed of. However, it would be a mistake to think my expertise is what gained my success or my hours. Rather, it was these hours that gained me my high level expertise. To get the hours started first with willingness. Since everyone begins as a non-expert, the fastest path to expertise is willingness to take opportunity and to generate chances for opportunity. I began in the fitness industry with the willingness to accept any duty. If the facility needed toilets cleaned before opening at 5am, I wasn’t too proud or too good to do it. If the pro shop needed the till counted before opening on a Saturday or Sunday, so be it. When members joined at 9pm, someone needed to meet them, interview and interact with them, welcome them and hear them, guide them, and instruct them. In my mind, all of these “menial” tasks were a path to understanding the total working machine of the fitness industry and ultimately gain more chances for more opportunities to advance my understanding ever further. I could. So I did. I can. So I do. Be willing. That’s first. And from that I find is a natural gravitation toward learning. I long ago lost track of speciality certifications, workshops, classes I’ve attended since working professionally in this industry. It’s in the hundreds. I spent a good portion of 2012 memorizing the entirety of the USMLE1 medical school lecture series. I shadowed cardiologists. I trained a lot of MDs and physical therapists and exercise physiologists and PhDs in Nutrition Science. I learned a lot from them along with teaching them a great deal. I ran workshops. I hired and developed a few hundred health and fitness professionals. I found early on that the more brilliant your employees and peers and clients, the more you could learn during every minute of work. I increasingly maximized. When I gained clients who were successful business people, I learned about business. When I took on clients with outrageous health challenges, I learned health troubleshooting. Every single second is a learning opportunity. Every. Single. Second. That is the “how.” The “why” is a little trickier. The short answer is I needed to. I never had a side gig. Fitness wasn’t a side hustle. I didn’t have backers or family money. When things went sideways in my wife’s workplaces or when we started a family, there was no alternative. I had to be the greatest who ever lived. I did not have an option to fail, to flail, to falter, to be average, or even to be pretty great. I had to be superb. And it helped to have some healthy competition and know that I had some peers who were busting their asses as well. Sadly, that is missing for too many influencers or fitness pros. They don’t have mentors or even genuine hard-working peers. So they are never going to mature into the potential they have. They don’t have anything to draw them up other than views or likes, which are, by definition, a hallmark of INexperience. When I worked at Bally’s, there was a pride in having the appointment book as full as possible. I could actually SEE what other trainers’ days looked like. When I obsessed over national reports, I was legitimately intent on being at the top of those reports. I could observe the number of sessions sold or serviced by hundreds of clubs across the country. I knew what it meant to be the best, and what it would take to beat the best. I could see some absolutely freakish performances and call those clubs and talk to those trainers or directors. Today, that spirit is gone. It’s been replaced by trying to have the greatest social media followings, which is largely a measure of how little genuine coaching experience you can even have. Think about it: you can either work; or you can post. You should do some of both. But the “reports” today are not reports at all; they are merely measures of popularity which reward only the marketing. That’s where the incentive is. So that’s where the “performance” remains. I have now coached a number of influencers who have never completely more than 25 appointments in a week, most do no more than that in a month. They monetize their followings and sell online programs. So there was never the incentive for them to book up on mentoring or direct coaching. They cannot ever achieve high level mastery of exercise science or nutrition or just progressive human movement with this low volume. It’ll take them 30 years to be where I was at in my first 5-10 years, but maybe even longer since there will be no intensive consolidation of experience. But they don’t have any spirit of competition around them to hone them anyway. Almost none are starting at high volume fitness centers. And they are burning up tons of hours on videos and posts at the BEGINNING of their “careers.” It’s actually quite sad, because I think I may be among the last generation of great coaches. The measure of expertise in human performance has been steadily shifting toward entertainment, not evidence-based, not empirical, not experience-driven facts. And the young coaches don’t even know it. They are comparing themselves against equally-inexperienced online personalities. Influencers online genuinely don’t know that they are actually quite terrible and should probably not be sharing their “insights”. And the overall market has no way to know this. For a lot of people, it would stand to reason that a guy with five million YouTube subscribers must be an expert, even if you have never seen him post a single calendar shot like mine, even if you’ve never seen him post videos with different clients, even if you’ve never seen him change an ounce of body composition or personal performance himself. So people have to understand there are two markets. There is the real world market where investors will support incredibly advanced strength coaches. I would include online and virtual coaching within this market. But then there is an entertainment market which has little to nothing to do with health and fitness. The up-and-comers and the veteran coaches alike need to make a decision about which market they want, because deep personal connections are not related to Facebook ads and ebooks. Again, you could do both. I admire those who’ve generated a fair bit of effort at each. But the massive experience with real world coaching is not going to come from bending over backward to make another post, to get more content, to shoot another video, to snap a few more shots. NONE of that is exercise science. None of that is valuable experience in strength coaching. It is cinematography experience. It is entertainment experience. It is moviemaking experience. More than anything, choosing the real world market is how you become the most consistently overbooked professional trainer and strength coach on earth. Don’t look at helping people as a temporary launch point to get to your next scheme. You have to look at training/coaching itself as the actual peak. It’s not a stepping stone. It’s not a layover. Coaching is the peak. And being an online famous person is not coaching. They are unrelated. They are in opposition, in fact. The way you become the most consistently overbooked professional trainer and strength coach on earth is you must first see that it is THE height. Be willing. Make every second a learning opportunity. Be ravenous to learn, dying of thirst for experience. If you crave online fame, that’s fine. Pursue that. But please don’t try to place yourself on the same level as me or professionals like me. If you crave opportunity and learning and experience, then you will be a genuine master, a true expert. And that’s how you’ll go on to excel in the real world with real people as a real teacher. Not just for a moment. But for decades.
0 Comments
Did You Know That "Light Physical Activity" Can Be More Fatiguing Than Heavy Weight Lifting?2/27/2024 Low force contractions induce more central fatigue and nervous system fatigue than high force contractions:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17626289/ This research demonstrates that long duration training of a low or moderate intensity is more taxing to the nervous system. Mechanistically, this aligns with our understanding of sympathetic activation. A stress state (of varying degrees) occurs during any training, any perceived anxiety-producing trigger, any prolonged activity. The stress hormone production, receptor down-regulation, and therefore CNS fatigue will have more to do with length of activity than load/intensity. Anecdotally or observationally, the lay audience can confirm this finding. Elite strength athletes are on average more recovered, less anxious, less irritable, less agitated, than non-athletes or elite ultra-endurance athletes. Gym-goers who emphasize short strength training (no matter how heavy) tend to suffer fewer CNS downsides than gym goers who emphasize lengthy routines. Orthopedic injuries (many of which stem from CNS fatigue) occur less in people whose workouts are heavy in load and short in duration than in those people whose workouts are lighter in load and longer in duration. Metabolic stress does some of the work and mechanical tension does a lot.
Beyond being in a state of caloric surplus, rested, and some more generalized debates over volume/intensity/progressive overload, the proposed processes which stimulate muscle growth come down to metabolic stress and mechanical tension. The old theory was muscle damage. “Break it down to build it up,” was a common bro-science aphorism. Not only isn’t it true, but it actually cannot be. No expert in the field affirms this anymore, because of the many counterexamples and obvious impossible paradox therein. Elongating muscles creates the greatest muscular damage, and training which emphasizes forced stretches and hyper-mobility does NOT improve muscular size or efficiency. The contrast of gymnasts versus yogis is perhaps the clearest example of how fixation on lengthening or over-lengthening muscle tissue does not result in a size, speed, or strength gain. Are there benefits to improving control of greater range of motion? Of course. But the very act of “relaxing into a stretch” instead of developing control in it and power over it means limiting mechanical tension, maximizing damage, thereby cutting the strength and size stimuli. Metabolic stress is real but harder to nail down. Contraction of skeletal muscle does produce myokines, alters energy uptake through changes in glucose transporters, and there are some real measurable reactions in hormone responses on site and throughout the person. The degree to which this contributes to overall health and fitness is significant. The precise muscle size impact from any one cascade is unclear, however. There are plenty of athletes who contract muscles millions of times at low tensions and have zero muscular development despite the metabolic stress contribution. See olympic and elite marathoners and endurance cyclists. This leaves us with mechanical tension. I have noticed a trend with upstarts in the past five years or so where they are obsessed with mechanical tension as the be-all end-all. And I’d agree that across decades of professional experience I MOSTLY see muscle size gains in response to mechanical tension. That is, as people truly encounter muscular performance limits, and barely eke out a last or genuinely failed rep, that is where we tend to see size gains most dramatic. The journey requires progressive overload, obviously. But the individual mechanism within a workout is the enhancing of mechanical tension. To be more clear, when a relatively rested person encounters a strength exercise in a stable position and performs 5-20 reps but only ends the set because the velocity of the movement grinds to zero, THAT is that person’s maximum mechanical tension for the intended muscle group of that exercise. However, I want to caution against a cult-like insistence on ONE way and only one way. The first reason for this is that we don’t KNOW for a fact that getting to absolute muscle failure is better than getting very close. And we don’t KNOW how much better (or if) very-close is than close. The second reason I caution people is that to be able to effectively get near muscle failure, you have to first develop expertise. And to become advanced and skillful (and retain said skill) you will have to train sub-maximally some of the time. Moreover, if people do not include some power, speed, and greater range of motion training into a program at some point, the participant is more likely to get hurt or discontinue, such that he or she can no longer gain the reward of mechanical tension. At this point, most people might be asking, “What does this translate into for my workouts?” Or, “how do I apply this?” Let’s take a machine chest press as an example. Imagine you are able to press about 200lbs on this exercise for around 8 reps. Let’s say we start this workout with this exercise, such that you are fully rested once getting to this piece of equipment. Potentially, you’d perform a set of 100lbs for 5 reps, very strictly and intent on creating tension and mentally connecting with the pecs, triceps and deltoids. Afterward, you might wait 3 minutes, and perform another sub-maximal set, 3 reps with 150lbs, perhaps. Wait another 3 minutes. Now, it’s time for business. You set up with all of your normal posture, cues, settings and mentally commit to getting 9-12 clean and toilsome reps with the 200lbs. The first 7 reps may be harder than you anticipate. 8 is grueling. At the 9th rep, it’s a serious question whether you can complete it or not, but, through gritting teeth and eating the pain, you get it. Now, you fight headlong into the 10th rep and the weight is grinding to a halt; but you continue pouring your every fiber of will into budging it another millimeter. And possibly it doesn’t go. You still go to war in your heart and drive your body in the back pad as the bones in your arms seem to bend against the impossibility of the handles. THAT is mechanical tension. THAT is one working set. And THAT alone is sufficient stimulus to get stronger and gain muscle size. Afterward, you might desire doing another few exercises for the same or similar muscle groups. There’s nothing wrong with that. Potentially, you could muster almost the same wherewithal for a legitimate working set like that on the same muscle group a few times in a whole workout sessions. If you include a separate muscle group, certainly you could. However, any degree of workout far in excess of that is not supported by evidence for the purposes of this simple discussion. Certainly, you could add many more exercises and sets and reps and alternate modalities, if you want to generate some more muscular endurance or train a variety of additional skills. But for muscle size, there isn’t a need to add lots of additional sets or exercises. In time, that chest press must be 210, 220, and 12 reps or more, BUT in the same manner, the same grind, the same intentionality, the same degree of battle. THAT is how muscle is actually built. In 2021, over 44,000 Americans died from taking a fall:
https://www.statista.com/statistics/527298/deaths-due-to-falls-in-the-us/#:~:text=The%20highest%20number%20of%20deaths,States%20was%2044%2C686%20in%202021. About 86% occur in adults over 65: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2804614#:~:text=In%202020%2C%2042%20114%20deaths,aged%2065%20years%20or%20older. But that means that over 6,000 occur in people under 65. This isn’t counting non-fatal fall injuries, which count in the millions. Almost every hip fracture and most traumatic brain injuries occur from falls. The number one risk factor is weakness: https://www.cdc.gov/falls/facts.html Literally, just become stronger, and in an increasingly greater range of motion; and you’ll nearly eliminate your risk of brain injury, hip fracture, and fall-related death: https://www.instagram.com/reel/C2XOEMBuW6m/?igsh=aW1mbmxkaDV1OG1p Even when you train and eat protein, you will eventually lose some muscle. And muscle loss is the primary contributor to loss of function with age:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2804956/#:~:text=Muscle%20mass%20decreases%20approximately%203,60%20%5B4%2C5%5D. The average is 3-8% of muscle lost per decade after 30, and that loss accelerates after 60. The implications of this cannot be overstated, as it is a causal contributor to loss of bone density, loss of insulin sensitivity (aka - becoming more prediabetic/diabetic), loss of stature, loss of balance, loss of most fitness and health markers. Weight loss doesn’t help. The average muscle and healthy tissue-loss during weight loss is 20%: https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/weight-loss-why-you-dont-just-lose-fat-when-youre-on-a-diet/#:~:text=A%20better%20determinant%20of%20how,to%20several%20kilograms%20of%20muscle. And it is not regained with weight gain. A person who has lost about 10lbs a few dozen times over the years has lost 2lbs of muscle, cartilage, and bone density multiplied by the same number of weight loss bouts. There’s a good chance there are 30 fewer pounds of muscle on that person, even if at the same body weight as before. There is less cartilage integrity in joints if she never lifted weights. There is less bone density. Thus, you can see that people who yo-yo in weight but don’t do resistance exercise and sufficient protein intake simply get weaker and less mobile as they age. It’s not simply that your risks of fall increase as you lose muscle, it’s that the degree of damage possible FROM THE FALL increases with loss of muscle: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10048873/#:~:text=With%20aging%2C%20muscle%20loss%20and,risk%20of%20falling%20%5B4%5D. I don’t need to enumerate the many signs of severe lean tissue loss. Inability to stand on one foot while you put a sock on the other is a decent measure. Getting on and off the floor without the use of hands is another. Handstands, pushups, pull-ups, cartwheels, full bridge, vertical jump, sprint speed, single leg squat, etc. There are many. Most “bad joints” are actually insufficient muscle. And even when the joints are indeed critically failing, you better believe that having piles of lean tissue around them makes the symptoms 1000% better. In 20 years of professional training and coaching, I have observed many people with “bad joints” get to performances they believed impossible simply by getting stronger and regaining some muscle. And this isn’t a plague of age. Young people are more susceptible to dislocations, collapse, and injury when they are detrained and have muscle weakness: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8403423/ There are a number of studies showing that lean tissue loss is a predictor of mortality: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6014293/ To be clear, how much loss of strength predicts IF you recover from anything, which includes respiratory infections, just fyi. After a certain degree of strength loss, people simply die. Strength loss is an independent predictor of mortality: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5820209/. Weakness literally kills people. Perhaps more perplexing to people, muscle tightness and perception of inflexibility IS weakness. Tight hamstrings are weak. Tight backs have weak abs and weak hip flexors and usually weak hamstrings to boot. Tight necks are incredibly weak necks and shoulders. Aching and falling arches are weak feet and ankles. You get the idea. Muscle is next-to impossible to gain or regain or even retain as a full-grown adult. That is, unless you consistently train to get stronger across years, and consistently eat sufficient protein intake for years. But the selection of exercise is also critical. Walking isn’t a muscle builder because it occurs on a vertical skeletal alignment. That does not train the capacity of the body when the thigh is horizontal. A bicep curl is not going to help a person to stand on one leg and pull the opposite knee into her armpit. It’s not that these are no-value exercises. They are just low value with regard to high function of the body. Avoidance of contacting muscles in the shoulder WILL worsen neck and shoulder problems. Strong necks and shoulders simply don’t ache. They don’t degenerate. They aren’t tricky. As such, the selection of exercises must be some sort of approximation of the intended physical capability which the person wants to regain AND a direct confrontation of where that person is already measurably weak. This is a more difficult confrontation than one might expect. People may trend toward a longer walk or a longer bout of cardio, reasoning that the longer duration or distance is an increase in physical fitness. People may love their arm circuit training or Tabata arm series. But these will do absolutely zip nada for genuine fitness. Spending even more time in an activity which cannot confer muscular development will not magically confer muscular development, no matter how long that person spends on the activity. Cardio doesn’t help much. It is catabolic, meaning it breaks down tissue. The intensity of muscular contraction is very low. The skeletal angles are such that the muscles never must produce much force. Ergo, it won’t shield from major muscle loss AND it will often accelerate it, UNLESS the person is measurably getting stronger in lifts week over week. And without going too far into the science, suffice it to say that the person must feel the intended muscle he or she is trying to develop AND generate such tension in it that there is a serious question about whether the rep can be completed at the end of a set. That, and pretty much only that, is going to spur on muscle building. If you used to be able to squat all the way down but now can barely bend your knees, you lost far too much muscle already. If you used to do handstands but now can barely reach your hands overhead, you lost far too much muscle already. If you used to not have stiff muscles but now they’re tight all the time, you lost too much muscle and strength. Long story short: if you have not intentionally been training to gain muscle or get more athletic, you have lost a lot of muscle and healthy tissue. And if you want to turn that around, it doesn’t actually need to be too involved. What are the physical abilities you’d like to build, rebuild, or retain? Work strengthening exercises specifically toward those. That’s it. Really. And when you work them, it is critical that you create enough tension in the muscle to communicate to the body that it must adapt. What that means is that you should not pick any ol’ rep range and then stop AT that arbitrary point. For example, if you pick up a weight which you can confidently perform for an exercise 10 reps, your objective is to commit to 11-20 controlled quality reps which end at zero velocity because your muscle can no longer generate any speed of the exercise. It absolutely does not matter what you read or heard about rep ranges. It doesn’t matter what you saw in a magazine or heard in a group ex class. Your muscle fibers only know if they’ve been taken near their performative limit. That. Is. It. If you move the weight quickly and with ease and end the set before your physiology has ground to a velocity of zero while trying earnestly to complete a repetition which it cannot, then you simply haven’t trained. You have not strengthened. You have not communicated to the body to gain, regain, or retain muscle. “Failure” isn’t really even the right term. There are too many common misconceptions about this concept. People will use momentum and kipping and cheating to nab another rep. That’s not it. Really, it’s just a matter of placing effort into the exercise until your will cannot make the muscles move the exercise movement one more millimeter. That’s the stimulus. The environment which will respond to that stimulus is one of sufficiency. Vitamins. Minerals. Water. Sleep. Rest. Protein. A whole lotta protein. If you can’t imagine eating 1 or more grams of protein per pound of body weight, at the very least hit .5. If you weight 100lbs, the absolute low-end bottom of healthy intake would be a half pound of meat or equivalent protein source daily. For obvious results, double or triple this. And perhaps one can see why even really well-intentioned and hard-working exercisers and health enthusiasts tend to fail completely at making significant and obvious physical progress. Lots of light weights shy of high effort won’t do much. Lots of cardio won’t do much. Lots of green veggies won’t do much. It’s not that any of those things are bad. It’s just that none of them yield a high ROI for the most needed facets of fitness. Intense weight lifting, progressively and consistently performed, with a diet rich in protein, and sufficient sleep and stress management will outperform pretty much any other trendy programming in existence. Otherwise, you’re going to lose muscle. MENS SANA IN CORPORE SANO.
“A healthy mind in a healthy body.” Almost two-thousand years ago a Roman poet named Juvenal penned a list of what is desirable in life; and the first sentiment on that list gave rise to the Latin maxim above. Mankind viewed caretaking of physical health as central to the mental and spiritual well-being of an individual. More modern thinkers began to run astray after Descartes described the mind as a separate essence from the body in the seventeenth century. Descartes was merely describing different aspects of a person. But subsequent theorists and psychologists like Freud proposed an increasingly disparate distinction, which we can openly see in many people’s worldview today. One could say humanity lost its way from the eighteenth to twentieth centuries, beginning to think of the spirit and the mind and the physical being each in unconnected silos. Practical successful therapy has not affirmed any such separation. Endocrinology and neuroscience has not affirmed any such separation. Rather, the arc of humanity came back to its senses in the present day. The deeper that researchers dig, the more our modern understanding affirms Juvenal and all those who came before him. We may utilize separate terms; but the highest state of our mental and spiritual health will be best reached by curating our physical well-being. “In everything that men do the body is useful; and in all uses of the body it is of great importance to be in as high a state of physical efficiency as possible. Why, even in the process of thinking, in which the use of the body seems to be reduced to a minimum, it is matter of common knowledge that grave mistakes may often be traced to bad health. And because the body is in a bad condition, loss of memory, depression, discontent, insanity often assail the mind so violently as to drive whatever knowledge it contains clean out of it. But a sound and healthy body is a strong protection to a man, and at least there is no danger then of such a calamity happening to him through physical weakness: on the contrary, it is likely that his sound condition will serve to produce effects the opposite of those that arise from bad condition. And surely a man of sense would submit to anything to obtain the effects that are the opposite of those mentioned.” - Socrates In the fifth century BC, the Greek military strategist and historian Xenophon recorded this account of Socrates in the third chapter of Memorabilia. In the fitness industry, many people have quoted a preceding section of the same chapter as a way to showcase the renowned philosopher’s endorsement of exercise. Indeed it is. But the chapter as a whole is far more than that. Look closely at the closing statement: a sensible person would submit to anything to avoid mental and physical deterioration. Anything. Anything. This year, presenters at the 2023 summit for the American College of Cardiology and the World Congress of Cardiology are arguing that 8% of deaths are attributable to lack of sleep. Low sleep quality raises risk of cardiac event by nearly 70%. The findings are not even yet published, but based on 172,321 people who participated in the National Health Interview Survey between 2013 and 2018, conducted by the CDC and National Center for Health Statistics. Though as of yet unpublished, these claims mimic prior published research indicating that insomnia and sleep disturbance rank among the top risks for heart attack [1.] For at least twenty-five hundred years we have known humans need sleep and humans need movement. These are two of the least provocative and least contentious sentences in health and wellness. They are so undoubted that they extend far beyond expert consensus to total unanimity. They are boring, really. But the questions of “how much?”, “how to implement?”, and “why?” open a broader discussion. That is where the interest lies. And that is where we must focus. The autonomic nervous system governs our expression of sympathetic and parasympathetic response. Otherwise known as fight-or-flight versus rest-and-digest, this relationship is tied quite tightly to risk of all-cause-mortality. Simply, during stress, heart rate rises and heart rate variability lowers. During rest, heart rate lowers and heart rate variability rises. Even modest decreases in sleep end up placing the body in greater sympathetic response THE ENTIRE DAY [2]. As such, we see contemporary studies this year finding that a single night of sleep deprivation ages the brain faster [3]. Essentially, when we persistently get low quality and short sleep, we consistently run the autonomic nervous system in sympathetic governance. There is absolutely nothing wrong with stress inherently, briefly. As Socrates said, we should attend to our fitness. Sympathetic response (as the reader will soon discover in the discussion on exercise) is part of a healthy life when accompanied by physical expression. When we need to fight or flee, absolutely we ought to do so. We ought to be able to do so. For a short duration. In fact, the short intense intentional stress of exercise appears to help bring about a subsequent parasympathetic counter-response in a symbiotic relationship covered below. In part, short intentional sympathetic response allows adenosine to tell the brain it is tired and ready for the wind down [9]. However, without sufficient sleep, by definition, we are in prolonged sympathetic agitation and unable to get all the benefits of repair and flourish from parasympathetic activation. “A peaceful heart leads to a healthy body.” - Proverbs 14:30 Years ago, studies on shortened telomeres in traumatized children gave us a clue. Unsurprisingly, then, researchers at Bar-Ilan University published findings in Nature in 2019 showing that sleep reduced DNA damage [4]. Now, the depth of this may not strike readers immediately. However, what we are talking about is slowing or reversing aging itself. What we are talking about is reducing cancer incidence. When we talk DNA damage or DNA resilience, we are talking the basis of progress and regress, growth and death, abundance or dearth. Whether we are discussing general stress, the accumulated cell damage we term “aging”, the accumulated errant cell proliferation we call “cancer,” or really any other negative experience in cell function, the crux of the matter rests firmly on chromosomal dynamics and DNA degradation. How we defend cells and rebuild health rests, quite literally, on rest. This is a significant problem, because the modern person sleeps less than in any prior period of human history. Historians and sleep researchers agree that it was entirely normal for adults, even peasants, to sleep nine to twelve hours per day regularly. Generally, they broke daily sleep into two periods, not one, which helps. Now, we can blame our single bout of sleep. We can blame the change on the incandescent lightbulb, as its widespread use aligns well with the historical timeline shift in human sleep loss. We can blame it on the Industrial Revolution and expectations of certain labor hours. And we can certainly have the discussion over blue light and work-life balance at some point. But where we lay the cultural, technological, or historical blame leaves us little workable solution anyway. None of us are totally revising the forward march of technology and modernity. Rather, we have an even bigger attached problem to address. We do not even get as much sleep as we think we do. A demographic-population-matched study of over two-thousand participants showed that, while people think they get a little over seven hours of sleep on average, they get closer to six [5]. Even our incorrect overestimate is too little. But our actual behavior is possibly half or less than half of what we genuinely need and historically used to get. It should come as no surprise. And it takes little leap of imagination or logic to see the connections to prevalence of disease, depression, and simply the overwhelming popularity of broken spirits in the world. Without adequate sleep, life is lived less vibrantly. And we can readily see the consequences of eight to ten generations in a row of increasingly sleep-deprived populations. Weight-loss studies gave us another clue to the stark divide between under-rested and adequately-rested people some time ago, as even when we account for energy/calorie matching, people who sleep more lose more of the weight from fat tissue than people who sleep less (and, therefore, lose a greater percent of weight from healthy tissue) [6, 7]. And this is not merely an observational conclusion. It turns out that the mechanism is known and understood. We are continuously making new cells. We first make progenitor cells, which will become the replacement to the old cells of whatever types we replace. When we are under-slept, under-rested, and over-stressed, the percent of the progenitor cells which become adipocytes (new fat cells) goes up a lot [8]. It is a sobering finding, showing us that sleep loss incurs measurable injury to hormonal functioning and the actual cellular life cycle within us. Juvenal and Socrates and Solomon and researchers are in agreement: to heal our spirit, we must heal our bodies. For this, sleep is clearly critical and low-hanging fruit. We could view it as the “yin,” so to speak; and, if so, then movement or exercise is the “yang” to our total wellness. Frankly, neither one exists well without the other. In terms of implementation, people struggle dearly when they endeavor to approach improvement in one and not the other. That is, there is ample evidence that exercise improves sleep [9]. Yet people with better sleep are more likely to exercise [10]. We can unpack those chicken-and-egg sequences, debate which should precede which until the cows come home, and really get nowhere fast. Fundamentally, we are not likely to make any headway until we embrace them as two halves of a whole, concurrently accessible, necessarily concurrent. Tribal societies, ancient cultures, and classical education models did not separate athletic expression from mental and spiritual pursuits. Like our reduced sleep, it is a very modern invention to think of the human condition as capable of its potential with reduced movement. Without exercise, we live smaller. 2008 might have been a crushing year for financial markets globally; but it was a banner year for exercise physiology for all mankind for all of time. The first myokine was identified, solidifying the theory that skeletal muscle is a hormonal/endocrine organ. Researchers at McMaster University provided powerful evidence that very short but intense bouts of exercise provide more/equal benefits to that of very lengthy exercise. And Dr. John J. Ratey, MD published the book, Spark: The Revolutionary New Science Of Exercise And The Brain. In Spark, Ratey exposed readers to some of the most recent neuroscience findings regarding exercise while repeatedly referencing the Naperville school district as an applied proof-of-concept case study. Essentially, cortisol crosses the blood-brain barrier, opening up pathways for neural damage, immune inadequacy or dysregulation, cognitive deterioration, emotional downturn, and all of the neurodegenerative diseases. One protection is BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor). Exercise is uniquely positioned to express BDNF. Literally, exercise makes us better in just about every way. It is pretty cut-and-dried, not a lot of controversy. Ratey added that Naperville has been far ahead of the curve with integrating athletics of an incredibly broad selection into their academic emphasis; and Naperville alone is the only place in America in about four decades which has been able to rank in international math and science testing versus Asian countries. Spark was great. Ratey was not wrong. But science has unpacked a lot more since 2008. Namely, intense effort is superior at BDNF expression [11]. Although Ratey was mostly convinced in the benefit of aerobic exercise, intense effort is king. We have since found that lifting to limit a weight that is 70% or even 90% of an individual’s 1-rep maximum causes significant rises in BDNF long after the exercise session is over [12]. This, of course, does not mean that people should exert at an unsafe effort or in an unsafe manner. Rather, relative to their personal ability, they should work up to intensities which are high for them. And, as we already covered above, adequate sleep must exist in order to be able to operate at intense physical levels. Each reinforces the other, in kind, over time, and a greater synergy between sympathetic and parasympathetic expression may reign. The brain-protective benefit is clear. The sleep benefit is clear. The progress benefit is clear. In conjunction, the yin and yang of sleep and exercise support and gird up one another, allowing the individual to explore his or her full potential. With intentional movement and improved sleep hygiene, cardiologists say we reduce our risk of heart attack. Geneticists say we reduce DNA damage. Neurologists say we improve our ratio of sympathetic to parasympathetic response. Socrates might say we have our strongest protection for our minds. And Juvenal said, MENS SANA IN CORPORE SANO. 1.) Sofi F, Cesari F, Casini A, Macchi C, Abbate R, Gensini GF. Insomnia and risk of cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2014 Jan;21(1):57-64. doi: 10.1177/2047487312460020. Epub 2012 Aug 31. PMID: 22942213. 2.) Castro-Diehl C, Diez Roux AV, Redline S, Seeman T, McKinley P, Sloan R, Shea S. Sleep Duration and Quality in Relation to Autonomic Nervous System Measures: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Sleep. 2016 Nov 1;39(11):1927-1940. doi: 10.5665/sleep.6218. PMID: 27568797; PMCID: PMC5070747. 3.) Chu C, Holst SC, Elmenhorst EM, Foerges AL, Li C, Lange D, Hennecke E, Baur DM, Beer S, Hoffstaedter F, Knudsen GM, Aeschbach D, Bauer A, Landolt HP, Elmenhorst D. Total sleep deprivation increases brain age prediction reversibly in multi-site samples of young healthy adults. J Neurosci. 2023 Feb 20:JN-RM-0790-22. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0790-22.2023. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36804738. 4.) Zada, D., Bronshtein, I., Lerer-Goldshtein, T. et al. Sleep increases chromosome dynamics to enable reduction of accumulating DNA damage in single neurons. Nat Commun 10, 895 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08806-w 5.) Silva GE, Goodwin JL, Sherrill DL, Arnold JL, Bootzin RR, Smith T, Walsleben JA, Baldwin CM, Quan SF. Relationship between reported and measured sleep times: the sleep heart health study (SHHS). J Clin Sleep Med. 2007 Oct 15;3(6):622-30. PMID: 17993045; PMCID: PMC2045712. 6.) Xuewen Wang, Joshua R Sparks, Kimberly P Bowyer, Shawn D Youngstedt, Influence of sleep restriction on weight loss outcomes associated with caloric restriction, Sleep, Volume 41, Issue 5, May 2018, zsy027, https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsy027 7.) Nedeltcheva AV, Kilkus JM, Imperial J, Schoeller DA, Penev PD. Insufficient sleep undermines dietary efforts to reduce adiposity. Ann Intern Med. 2010 Oct 5;153(7):435-41. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-153-7-201010050-00006. PMID: 20921542; PMCID: PMC2951287. 8.) Bahrami-Nejad Z, Zhao ML, Tholen S, Hunerdosse D, Tkach KE, van Schie S, Chung M, Teruel MN. A Transcriptional Circuit Filters Oscillating Circadian Hormonal Inputs to Regulate Fat Cell Differentiation. Cell Metab. 2018 Apr 3;27(4):854-868.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.03.012. PMID: 29617644; PMCID: PMC5889123. 9.) Banno M, Harada Y, Taniguchi M, Tobita R, Tsujimoto H, Tsujimoto Y, Kataoka Y, Noda A. Exercise can improve sleep quality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PeerJ. 2018 Jul 11;6:e5172. doi: 10.7717/peerj.5172. PMID: 30018855; PMCID: PMC6045928. 10.) Baron KG, Reid KJ, Zee PC. Exercise to improve sleep in insomnia: exploration of the bidirectional effects. J Clin Sleep Med. 2013 Aug 15;9(8):819-24. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.2930. PMID: 23946713; PMCID: PMC3716674. 11.) Gibbons TD, Cotter JD, Ainslie PN, Abraham WC, Mockett BG, Campbell HA, Jones EMW, Jenkins EJ, Thomas KN. Fasting for 20 h does not affect exercise-induced increases in circulating BDNF in humans. J Physiol. 2023 Jan 11. doi: 10.1113/JP283582. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36631068. 12.) Church DD, Hoffman JR, Mangine GT, Jajtner AR, Townsend JR, Beyer KS, Wang R, La Monica MB, Fukuda DH, Stout JR. Comparison of high-intensity vs. high-volume resistance training on the BDNF response to exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2016 Jul 1;121(1):123-8. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00233.2016. Epub 2016 May 26. PMID: 27231312. Multiply this by 50 weeks and 20 years. There were years where I worked all 52 weeks. And there were many weeks in there where I had 55-65 appointments PLUS another 20-50 hours of management time. But I’ve also had a few reserved years where I refuse to take more than 35 appointments in a week, and where we had multiple trips or went to Greece for 3 weeks. All the same, when you add in my studies, my daily medical and scientific journal reading, my own workouts, it is A LOT of deep deep knowledge, wisdom, and experience. I conservatively place it over 70,000 hours. It could be closer to 85.
In that time I’ve discovered really wild and unexpected troubleshooting, difficult outlier challenges, rare conditions, and many insights which just cannot exist within any lesser amount of experience. There are conditions and client challenges I did not encounter in my first 8 years which I’ve many times now encountered in the past 12. And I managed gyms with thousands of members in my first 8 years in this profession. So it gives me some worry. It gives me some worry because there are now a lot of really influential people online with far less experience than I had in my first 10 years, far less even than I had in my first 5 years, or even 2, less perhaps than I had logged as a kid when I was obsessed with reading nutrition science and exercise science textbooks. And these are the voices setting the tone out in the public, out in the ether, out in parlance. It’s not all bad necessarily. It’s even sometimes flattering to see a fitness trend nowadays which I had pioneered a decade or 2 prior. Whole franchises, companies and cultural movements today are built atop metabolic experiments I ran 10, 20, 30 years ago. But it’s also disappointing to see such simpleton explanations trending, such bad science trending, such bold and wrong advice trending, such entrenched insistence that one single cult is the only way. I don’t have the will to combat it. I am busy being a real business owner with a real business and a real storefront in the real world. So I’m not wasting effort on the optics of marketing and “looking” like a trendy online personality. But I will take the time from time to time to post and share something which I hope impacts even one person or corrects one of the many pieces of popular and terrible advice floating around. Today, it’s simply this: 1.) be honest 2.) track 3.) go slow 4.) persist 5.) progress And if I had to add a 6th, it would be to remind yourself that the distance between where you are and where you want to be is FINITE and involves ACTION which is broken down into measurable objective steps. Health and fitness or careers and business aren’t magic. They are not supernatural. Are there some tricks? Sure. Are there intense techniques? Sure. I have many. I share quite a few. But categorically NO ONE is going to shake those 5 truths. I saw it in this week. I saw it in the past few decades. To get anywhere worth going, we need to be honest with ourselves. Chances are high that when we are unsure why we aren’t more successful or further along or closer to goals, the first area we must examine is our personal honesty. Then, we need to be tracking what we actually do and measuring how it will or won’t produce the desired outcome (honesty, too, will be paramount here). Implementing productive steps need to be slow. We can always accelerate if we have good footing. But we sometimes can’t even reclaim where we were if we go too fast, get hurt, or burn out. If an effort works, it does not magically keep working. Not to be too circular, but we have to keep working at what works for it to keep working. I suspect honesty and persistence together may do more than the other three combined. As we grow, we earn more growth. With each step, we can tolerate more. And with each step, the distance to the goal is closed. With each step, the distant is closer. And soon, the unknown is the known, the unbelievable is reached, the seemingly-unattainable is attained. And that’s being incredibly, generously kind. Researchers at Harvard just committed academic fraud, sifting responses of 22,000 people who overate and developed type 2 diabetes, then lied and connected red meat, not overeating, to the development of diabetes:
https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/press-releases/red-meat-consumption-associated-with-increased-type-2-diabetes-risk/ Their own study does not support the claim. It is a scientific and biological impossibility. When you dig further into their inclusion criteria, you find they defined lasagna and ham sandwiches as red meat. They defined a Big Mac with fries and a large coke as red meat. This is actually a really good example of how liars or idiots can abuse epidemiology to try to claim something which is scientifically known to be impossible. A disease caused by excessive and persistent elevated blood sugar toxicity CANNOT be caused by something which DOES NOT RAISE BLOOD SUGAR. Red meat has a glycemic index of ZERO. But the flour in lasagna has a GI of 70 and the whole wheat or white bread on a sandwich is a GI of 70-100. In fact, the addition of the meat to the lasagna or sandwich actually LOWERS the glycemic impact, reducing the glucose volatility and toxicity which causes type 2 diabetes. The idiots/liars used a dataset of more than 200,000 people to find 22,000 people who overate carbohydrates and calories to give themselves diabetes. The liars stratified results to make it appear like red meat and not overeating gave those 22,000 their diabetes. They did not control for the fact that more smokers ate these “red meat” meals. They did not control for the 30 oz drinks of high fructose corn syrup included in these “red meat” meals. When you observe the nature of the “study,” realizing that data collection amounted to little more than self-reporting questionnaires, you wonder how anyone could take it seriously. It’s an incredibly flawed study to begin. But as you dive into the data, what this actually means is that there were more than 22,000 people who ate more red meat and didn’t get diabetes. The dataset actually proves the precise opposite of the headlines. Red meat was associated with a statistically significant DECREASED risk of diabetes when controlling for other variables (as actual smart people or legitimate scientists would do). Either through malice or ineptitude, these liars/idiots DID NOT control for the overeating of all food. The cause of type 2 diabetes is known: persistently elevated and unregulated blood sugar. Red meat has NO carbohydrates and rates ZERO on the glycemic index. It will actually reduce the glycemic impact of carbohydrates eaten concurrently. We actually already knew for an indisputable fact that red meat decreases risk of diabetes. American consumption of red meat has plummeted EXACTLY as type 2 diabetes prevalence has skyrocketed. American red meat consumption dropped like a rock since 1976, landing it today at an all-time historic low: https://www.nationalchickencouncil.org/about-the-industry/statistics/per-capita-consumption-of-poultry-and-livestock-1965-to-estimated-2012-in-pounds/ In 1976 only 2% of Americans had type 2 diabetes: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/circulationaha.106.613828#:~:text=The%208%2Dyear%20incidence%20rate,and%205.8%25%20in%20the%201990s.&text=Study%20subjects%20consisted%20of%20women%20and%20men%20aged%2040%20to%2055%20years. But as of 2022, at least 11.3% of American adults have type 2 diabetes: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/type-2-diabetes-mellitus-prevalence-and-risk-factors/print#:~:text=Other%20national%20databases%2C%20such%20as,undiagnosed%2C%20and%2095%20percent%20of Through the course of dropping our red meat consumption in half, we have increased our incidence of diabetes by nearly 600%. Public health expert, Zoe Harcombe, PhD, enumerated 14 flaws with the study which should have barred it from publishing: https://www.zoeharcombe.com/2023/10/red-meat-type-2-diabetes/ Her summary: 1) the inaccuracy of Food Frequency Questionnaires. 2) the reported intakes were ‘calibrated’, which increased risk ratios. 3) the definition of red meat included sandwiches and lasagne. 4) the serving sizes have changed since the original FFQs. 5) the intakes used to compare people have become more extreme. 6) the study claimed that women consume more red meat than men; that would be a first. 7) total red meat was claimed to have a higher risk than both processed red meat and unprocessed red meat. Total red meat is the sum of the other two. It can’t be worse than both. 8) the healthy person confounder. The red meat eater had a higher BMI and was more likely to smoke and less likely to exercise. We can’t adjust for a completely different person. 9) the reported calorie intake was absurd. 10) the characteristics table reported all food intake except the relevant ones – sugar and grains. 11) the headline claims did not adjust for the higher BMI. 12) even if there were no issues 1-11, the study could only suggest association not causation. 13) the relative risk numbers grabbed the headlines; the absolute risk differences were a fraction of one per cent. 14) the plausible mechanisms proposed applied far more sensibly to the bun, fries and fizzy drink (which were ignored) than to the burger. Largely, Harvard researchers are sloppy. More rigorous academics at Washington University took a much closer look at years of red meat and health research to find no good connection between red meat consumption and any health concerns: https://bigthink.com/health/red-meat-cancer-not-health-risk/ Unsurprisingly, some of the same Harvard researchers involved in this latest fraudulent academic work took umbrage with Washington University’s research. In fact, when Texas A&M affirmed the fact that red meat does not have a causal connection to health risks, faculty at Harvard began to gaslight those at A&M. Since the Harvard faculty didn’t have the intellectual honesty or capacity to present legitimate arguments against Washington or A&M’s studies, the Harvard faculty resorted to ad hominem attacks, accusing them of outside influence. This is more than an irony when Harvard leads all universities in foreign and corporate funding. In return for the personal attacks, the A&M chancellor called upon the president of Harvard to perform an ethics review on several of the Harvard faculty involved: https://www.tpr.org/news/2020-01-29/texas-a-m-harvard-scientists-feud-over-controversial-red-and-processed-meat-study The reader should understand that Harvard’s T.H. Chan School of Public Health is a criminal enterprise, having been forced to pay back over 1.3 million dollars which it stole from the NIH: https://www.justice.gov/usao-ma/pr/harvard-university-agrees-pay-over-13-million-resolve-allegations-overcharging-nih-grants Chinese faculty at Harvard have been charged with espionage: https://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/harvard-university-professor-and-two-chinese-nationals-charged-three-separate-china-related The total amount of foreign influence at Harvard is incalculable. But what we do know is that the T.H. Chan School of Public Health once received a 350 million dollar gift from a billionaire Chinese family: https://www.forbes.com/sites/chloesorvino/2014/09/08/hong-kong-billionaire-brothers-to-give-350-million-to-harvard-university/?sh=3d27e05d11b1 It’s long been time to reevaluate whether any of Harvard’s public health research is trustworthy. Now we need to take a look at whether we should allow them any more funding. Moreover, what's clearer than ever is that none of us have anything to worry about with red meat in and of itself. We can get into discussions about the accompanying foods and quality of the meat, or even the sustainability concerns. But we need to be done with the doom prophets and ideologues vilifying a single whole food as the culprit in diseases which are undeniably connected to excessive consumption of processed foods. My daughter ran into the room to have us quiz her Spanish vocabulary. My son couldn’t wait to be tested on the first 41 elements he’d just memorized from the periodic table.
Knowledge loves to be challenged. Discovery yearns to improve where it hasn’t yet explored. Authority, however… not so much. People ask me why we do a certain movement, training, or nutritional strategy; and I love that. People ask me how; and I love that. People challenge it. I love that. People bring up, “but I’ve heard…”; and I love that. “But so and so says…”; and I love it. I invite testing. I pray for it. Because I am an expert. Please, come test the limits of my mastery; and I will readily admit where I don’t know. No hesitation. No bluff. In fact, I don’t mind learning a BETTER way to do it. But some “experts”… not so much. And that’s why I put quotations around the title. People hide behind their names, titles, suffixes, education, franchises, organizations, or even hashtags like #trustthescience in an obvious effort to NOT be tested. They just straight up will not entertain inquiry. They recoil and shrink at the tiniest inference of scrutiny. That, by definition, is not expertise. I try to imagine a master martial artist claiming his technique cannot get any better, but also refusing to get in the ring, EVER. I cannot do it. It's silliness. But for some reason societally we will tolerate the very same tactic when employed in certain academic, scientific research, or political debates. It's actually more silly in those scenarios, as the person in question is making a claim to impose on our beliefs or behaviors. The master martial artist is merely claiming that his own technique cannot improve at all. I can recall talking to clients whose nutritionists and doctors countered my dietary advice all the way back to 2004. I always loved it and still do. The American Diabetes Association and Academy of Nutrition And Dietetics, which are wholly owned by industry (1,2), have long proclaimed opinions which are at odds with verifiable science. Whenever people challenged me on this, I’d just tell them to buy a glucometer. Once you DO science, you get unshackled from worrying about opinions. I right now have a client who is reversing her diabetes. There are “experts” in those organizations who will say it’s impossible; and all I can see is someone with very limited experience, and even more limited vision and imagination. Titles are great. Official licensure and proper education is necessary even. But wherever it is abused to avoid questions, we find lack of expertise. In my area of expertise, I continually find many areas of opportunity, for new learning, for improvement. And on average I have thirty-thousand to fifty-thousand MORE hours of professional experience than most of the top “authorities” in my field. I find it brazenly deceitful, therefore, when anyone in any area of health sciences and wellness declares a matter settled, rejecting the cornerstone of learning that IS inquiry. It’s never settled for experts. Static knowledge which cannot be questioned is only for the novices, the ignorant, the phonies, and the liars. Expertise invites testing. 1.) https://diabetes.org/about-us/research/pathway/supporters/corporate-sponsors 2.) https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/public-health-nutrition/article/corporate-capture-of-the-nutrition-profession-in-the-usa-the-case-of-the-academy-of-nutrition-and-dietetics/9FCF66087DFD5661DF1AF2AD54DA0DF9 The Revolving Door phenomenon, characterized by the seamless transition of personnel between regulatory agencies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and the private companies they are tasked with overseeing, has been a subject of intense scrutiny. This practice, exemplified by specific cases of influential individuals who have moved between public and private sectors, raises critical questions about conflicts of interest, potential regulatory capture, and the integrity of public health institutions.
The roots of the revolving door phenomenon can be traced back to the early days of regulatory agencies. Initially modest and resource-limited, agencies like the FDA and CDC sought expertise from industry professionals as they expanded. Over time, this practice evolved into a routine exchange of personnel between public and private realms. There are actually too numerous of examples to begin to cover in a short blog entry. To give the reader an idea of what this looks like, we will keep it to a short list of seven cases at the CDC and FDA, and a quick reminder of the trend we have now seen with NIH directors. Consider well the financial implications in a variety of other scandals and outright criminal efforts by large companies. Then, the reader should dwell on the influence of funding, regarding the manipulation of studies, the bribery of experts, and the advertising to the public. Finally, the reader ought to contemplate the concurrent shift in science toward stratified datasets instead of empirical biologic studies. It began with the tobacco industry’s efforts to rescue itself in the 1950s, but now this permeates all discussions on science to a degree wherein we forget that there are immense pitfalls to solely relying on human random controlled trials. That is, when we want to study the safety or danger of certain substances and techniques, we tend NOT to look at the cellular response inside humans anymore. Instead, we now tend to gather large datasets on people with specific reporting criteria which can be manipulated with great ease. As if taking a page directly out of the tobacco companies’ book on misdirection, many people will now sweep aside discussions of toxicology and mechanism, requiring “proof” in the format of epidemiology alone. And, as valuable as epidemiology can be to help reduce uncertainty on various investigations, it cannot prove safety, it cannot prove causation, it is not superior to empirical experiments, and it will never be the scientific gold standard or capable of eliminating the need for case studies, clinical experience, and the hard sciences. Scott Gottlieb, a former FDA Commissioner (2017-2019), is a prominent figure in the revolving door narrative. Before leading the FDA, Gottlieb was a resident fellow at the American Enterprise Institute, a think tank with corporate ties. After his tenure at the FDA, Gottlieb joined the board of directors at Pfizer. Andrew von Eschenbach served as the FDA Commissioner from 2006 to 2009. Following his tenure, he joined BioTime, a biotechnology company, as a member of the board of directors. Margaret Hamburg held the position of FDA Commissioner from 2009 to 2015, overseeing critical regulatory decisions. Prior to her role at the FDA, Hamburg was on the board of directors for Henry Schein, a global distributor of healthcare products. Julie Gerberding, the former Director of the CDC from 2002 to 2009, is another notable case. After her tenure at the CDC, she assumed the role of President of Merck's vaccine division. Tom Frieden, former CDC Director (2009-2017), provides another illustrative case. After leaving the CDC, Frieden joined the global health initiative Resolve to Save Lives. While not a private company, this move highlights the transition from public to quasi-private sector roles. His compensation in this role was reported to be at least $300,000 annually. Brett Giroir, who served as the Assistant Secretary for Health at the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and played a crucial role in COVID-19 testing efforts, joined the board of directors at Cue Health, a health technology company, shortly after leaving his position in the federal government. Former FDA medical officer Curtis Wright, who approved Oxycontin, went to work for the very company who made the drug two years later (and it just so happened that the drug maker’s efforts to woo him before the approval are well-documented). While not directly related to the revolving door phenomenon, it is worth noting that some members of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have substantial net worths. Dr. Francis Collins, the former director of the NIH, is estimated to have a net worth exceeding $5 million. Dr. Anthony Fauci, the longtime director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), has an estimated net worth exceeding $11 million. These are openly disclosed valuations based on public records, which do not include ties to other assets, and certainly not any shielded or hidden wealth in international holdings, influential networks, or digital currencies. This is just the tip of the iceberg. British medical doctor, Richard Smith, chief editor at the British Medical Journal for 25 years, Fellow of the Academy of Medical Sciences, warned us that scientific journals themselves are merely extensions of the marketing arm of pharmaceutical companies: https://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.0020138 And we must add to that awareness the fact that at least 70% of published peer-review research cannot be replicated: https://www.nature.com/articles/533452a Moreover, it is the wrong and worst research which is cited most often: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abd1705 Consensus scientific opinions are predominantly based on the preponderance of papers and those most-cited. Thus, we can see that in addition to the revolving door, we have the added disappointment that journals themselves are a marketing apparatus, that most of the research is not very good, and that specifically dubious research is what is often guiding the beliefs even among experts. And then that state of affairs leads us to tribalist arguments out among the citizenry, when instead we all need to be working together collectively to put the screws to every authoritative organization and human health directive in existence. These are not isolated affairs. Professionally, I have been combatting anti-science from authoritative health organizations for two decades. Years ago, I had to contend with provably wrong diabetes recommendations by the American Diabetes Association and The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. Both recommended styles of eating which will give you diabetes. The food pyramid appears to have been crafted with the intent of giving most of the populace metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Eventually, I just resorted to cold hard experimentalist science instead of arguments. I had diabetic clients test pre and postprandial (after eating) glucoses with different food selections to see for themselves which types of eating reduced blood sugar volatility. Unsurprisingly and totally predictably, they could see for themselves that their doctors and dietitians were not even close to correct. Obviously, low carb and higher dietary fat works the best. I’ve said it before, and I’ll say it again: don’t believe me; don’t believe your expert; DO THE EXPERIMENT YOURSELF. Empiricism annihilates theories and dogma and ideology every time. In the ten to fifteen years since, both organizations walked back their policies on 130 grams of carbs per day (or more), which used to be on their websites. But neither affirm the UK research done at Newcastle University which proves that type-II diabetes is reversible. Think about that. The ADA and AND are still in the Dark Ages. Why? Well, even the funding disclosure on the ADA’s website admits to over $53.6 million from corporate donors, which reads like a veritable Who’s Who of drug makers: https://diabetes.org/about-us/research/pathway/supporters/corporate-sponsors And the Academy of Nutrition And Dietetics is completely captured by the food industry: https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/public-health-nutrition/article/corporate-capture-of-the-nutrition-profession-in-the-usa-the-case-of-the-academy-of-nutrition-and-dietetics/9FCF66087DFD5661DF1AF2AD54DA0DF9 We could go on. And I have previously. I have written about the refusal of “experts” to acknowledge diabetes reversal here: https://www.elev8wellness.com/wellblog_best_nutrition_training_coaching_experts/type-2-diabetes-reversed-yet-again-in-medical-research And here: https://www.elev8wellness.com/wellblog_best_nutrition_training_coaching_experts/type-2-diabetes-entirely-reversible Sadly, we are only just getting started. The American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology were caught with their pants down in 2013, when they decided to recommend another 14 million Americans get on statins: https://www.huffpost.com/entry/health-news_b_4398304 The whole situation is one of the most flagrant and worrying examples of corporate capture, as not one independent biologist or biochemist on earth agreed with the proclamation, and most researchers rebuked the guidelines. Somehow, Google results today will not even return searches for the AHA or ACC scandal. At the time, scathing criticism abounded. Today, the internet has been scrubbed. A diligent effort on search engines probably can no longer get the reader to find the very article attached above. That's really saying something, because even the Annals of Internal Medicine showed that statins DO NOT REDUCE RISK: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/abs/10.7326/0003-4819-153-6-201009210-02004?journalCode=aim At the very least, the attempt to put millions of additional people on a profit-making drug for the next several decades should be a bit of an eyebrow-raiser. But I find most people don't even recall the scandal. The AHA made no apologies or revisions, and continues to receive over $30 million yearly from drug makers: https://www.heart.org/-/media/Files/Finance/21_22_Pharma_Funding_Disclosure_0323.pdf Another $690 million comes from “non-corporate” donors, which can and does include individuals who have ties to the very companies which benefit from AHA and ACC recommendations. And these overt conflicts of interest at the AHA and ACC lead to objectively incorrect information about human health in their printed and online materials. I’ve tackled this before: https://www.elev8wellness.com/wellblog_best_nutrition_training_coaching_experts/cardio-raises-blood-pressure-heavy-lifting-does-not The collective memory of the public is short. And the willingness of news organizations to spend any meaningful time on these stories is nearly nonexistent. Rapidly, people forget the scandals, even big and public ones, like when the World Health Organization faked a swine flu pandemic in 2010 in order to line the pockets of vaccine manufacturers: https://www.science.org/content/article/facing-inquiry-who-strikes-back-fake-pandemic-swine-flu-criticism It is helpful to remember the cautionary tale of Barry Marshall's research on H. Pylori at this juncture. In 1980 he proved that the infection causes ulcers. However, antacids were a multi-billion dollar business; and, as hard as it is for us to imagine now, antibiotics were not a profit model for pharma companies. Drug makers were pushing ahead with antacid medications, despite concerns that they caused cancer: https://www.bloomberg.com/news/features/2023-02-15/zantac-cancer-risk-data-was-kept-quiet-by-manufacturer-glaxo-for-40-years#xj4y7vzkg And the larger scientific community rejected Marshall's work. In fact, in 1983 his peers did not allow him to present his findings. Meanwhile, with antacid treatments, peptic ulcer patients were being permanently damaged by not having access to the cure. Then something magical happened in 1985. Antibiotics became profitable thanks to their newfound widespread use in agriculture: https://www.theworldcounts.com/challenges/consumption/foods-and-beverages/antibiotics-used-for-livestock At last check, the antibiotic market commands about $45 billion per year, and still growing. This provided a more conducive landscape to allow the discussion of Marshall's work through the late 80s and into the 90s. We take it for granted today that ulcers are to be treated with antibiotics, especially after Marshall gained a Nobel Prize in 2005. But the profitability of antacids versus the ever-increasing difficulty in making a profit model for human antibiotic sales almost prevented the science from ever being known. The severe conflicts of interest in these and other health-related organizations place us all in difficult terrain. We have reached a tipping point, wherein, as much as any of us would like to trust some of the declarations of the FDA, CDC, WHO, NIH, ADA, AND, AHA, ACC, NAS, and on and on the list goes, we simply cannot. We cannot trust these modern day priests and churches any more than any of us could trust the medieval authorities. They are too wrong too often. They are too tied to plutocratic control. And we have no major counteroffensive or safeguard other than intense, unrelenting distrust. The stakes for their mistakes and misdirection are too high. Gone is our former hope that the press would provide a bulwark against the strategically misleading efforts of major profiteers. Deep pockets influence the very stories and ideas we are even allowed to see. The US is the only country on earth that allows widespread direct-to-patient drug advertising. By 2016, pharmaceutical companies allocated $6.4 BILLION to advertise drugs: https://publichealth.jhu.edu/2023/spending-on-consumer-advertising-for-top-selling-prescription-drugs-in-us-favors-those-with-low-added-benefit#:~:text=Since%201996%2C%20annual%20direct%2Dto,promotional%20spending%20for%20pharmaceutical%20drugs Keep in mind that these are the known and direct marketing numbers. This does not include those “non-corporate” individual influential dollars we covered previously. This does not include the revolving door. This does not include all of the funding for that non-replicable research that comprises 70% or more of the papers in science. Really think about this. Think about the astronomical figures we are talking, just to influence purchase. Think about the implications. Think about what this must mean in terms of which candidates, and experts, and messages the media outlets are even allowed to air for us. It leaves a pretty dystopian landscape, since there is no clear way out. Every time We the People might band together to combat corruption, we end up fighting each other instead, while handing over more power to the corruption we should fight. The political fissure in America is illustrative of how everyone ends up supporting the same bedrock problem at one point or another. Conservative groups empowered wealthy corporate messaging in 2010, hidden within the guise of free speech (#citizensunited). Liberal groups empowered wealthy corporate messaging in 2020, hidden within the guise of science (#trustthescience). And around the circle goes. Political and ideological tribes keep empowering the same exact wealthy corporate messages, all while thinking they are making an appeal to some higher values. I am still a bit astonished at the willingness of so-called conservatives to defend corporate profiteering, and even more astonished at the willingness of so-called liberals to defend corporate profiteers. The former is not CONSERVing a free market. The latter is not LIBERAting the general public from misinformation and control. Republicans and democrats are running around going to bat for the exact same wealthy powerhouses. How is any defense of a giant multi-national corporation in line with support for a Republic or a Democracy? Pfizer is not the good guy simply by being involved in a form of capitalism. Pfizer is not the good guy simply by being involved in a form of science. Pfizer, or any of these giant organizations whose only interest is in power for itself, is not the good guy. Ever. Not today. Not yesterday. Not tomorrow. Not almost. Not by a long shot. Not that anyone should need a reminder, but the companies who own the messaging of our would-be regulatory agencies are by and large criminals. Literally. Pfizer was ordered to pay $2.4 BILLION for healthcare fraud in 2009: https://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/justice-department-announces-largest-health-care-fraud-settlement-its-history Pfizer lied in marketing of drugs: Pfizer illegally bribed overseas businesses for years: https://www.reuters.com/article/us-pfizer-settlement/pfizer-settles-foreign-bribery-case-with-u-s-government-idUSBRE8760WM20120807 And, of course, it is not Pfizer alone. Merck was caught in one of the largest fraud schemes in history: https://www.justice.gov/archive/opa/pr/2008/February/08_civ_094.html Purdue and Sackler are still in negotiations over their $6 billion settlement regarding the bribery of the FDA and knowingly creating the opioid epidemic: https://www.npr.org/2022/03/03/1084163626/purdue-sacklers-oxycontin-settlement The big 3 were settling on a combined $26 billion for their parts in the opioid epidemic which is already responsible for half a million American deaths: Johnson & Johnson was ordered to pay $2.2 billion for having bribed doctors and pharmacists: https://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/johnson-johnson-pay-more-22-billion-resolve-criminal-and-civil-investigations Hopefully, you get the idea. But if you don’t, feel free to search every single drug manufacturer and “fraud,” “lies,” “bribery,” “kickback,” and related phrases. There are thousands of cases. Here’s a short list of some settlements regarding false claims, Medicare fraud, and bribery: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_largest_pharmaceutical_settlements However, all of a sudden, when the pharmaceutical industry appeared to have found itself on the “correct” side of political debate during the pandemic, many people who would normally pride themselves on distrust of pharmaceutical industry, ironically, vehemently defended the pharmaceutical industry. More than that, defenders of the corporate profiteers vilified their own countrymen who dared to ask if we should be so trusting of pharmaceutical interests. That’s a problem. And it remains a problem even when we move our focus from the Pfizers of the world to the regulatory agencies or official organizations who are supposed to be disinterested groups, because, as I painstakingly detailed above, they are NOT disinterested. They are merely arms of the marketing apparatchik of the drug manufacturers and industrial giants of the world. My hope had been that sober and moderate minds would move increasingly back to a default position of extreme skepticism against wealthy corporations once the tribal rhetoric died down. But three-and-half years after the peak pandemic worry, well into the endemic phase, I’m not so sure. In daily conversations I find that people won’t really acknowledge the fundamental problem with choosing an ideological or political side. They like their sides, even when it means allying themselves with the pharmaceutical industry or wealthy corporations. They keep to their sides, even when confronted with irrefutable contrarian evidence. Look no further than discussions on vaccines, and you find almost no one who can manage to place himself or herself in a third camp. People immediately stake out a “pro” or “anti” position, and this tends to be informed first by what type of virtue someone wants to signal or which political camp with which someone prefers to be associated. That’s not actually how science works. There are risks AND benefits. AND different drugs or vaccines carry different ratios of risks and benefits. Nowhere does there exist a space to be “pro” or “anti” with regard to an entire category of unrelated or variant substances, especially by tribalist pressures. Some of X may be good. Some of X may be bad. Science does not have a place to be 100% pro-X all the time. Science does not have a place to 100% anti-X all the time. Each particular individual substance must be individually evaluated; and each one will have different degrees of risk or effectiveness. The resistance against nuance, or new or different ideas is not shocking. Over the past two decades as a health and fitness professional I have seen people refuse to budge off of clearly anti-science beliefs around the “badness” of cholesterol, or salt, or saturated fat, or red meat, or youth weightlifting, or fill-in-the-blank-here. People really like their tribes. People really want to side with wealthy corporations even while in the very act of saying they do not. The tipping point has brought us to a place where that type of simpleton sidism simply will not do. The sides and tribalism and the ardent defense of really big pocketbooks is not advancing any of the common people. A brief look at American health statistics will show that none of the popular medical advice or popular health and fitness advice has been productive. It is the opposite of effective. It is embedded in a backdrop of ideological and political division, a ruse to keep the majority of people at each other’s throats, distracting us from the rampant corruption and corporate control of messaging. That’s just the stark health outcomes. When we expand our view to look at how wealth is distributed and how real purchase power of the middle class has evaporated since the 1970s, we can see that there is a concerted effort to consolidate all power and money in a tiny oligarchy which effortlessly pits the whims of common folk against each other. It should come as no surprise then that empirical science is generally not even discussed. The framework for nearly every human health science debate is our interpretations of epidemiological tables, NOT experiments which could be observed and replicated and tested and verified or disproven. That’s new. That’s engineered to fit perfectly with the revolving door, conflicts of interest in funding, advertising, and monopolistic control of messaging. That’s a problem. The tobacco industry left an indelible mark on science, even if it ultimately failed to exonerate itself in a court of public opinion. From the 1950s to the 1970s tobacco industry interests set about swaying scientific opinion merely through funding. That is, they knew that if tobacco companies set out to fund research, it would just so happen to be increasingly LESS critical of the tobacco-cancer connection: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2598497/ Categorically, what occurred in this period of time was a vehement insistence on epidemiology instead of biologic studies. If you subject human cells to smoking, asbestos and tar in a laboratory, it’s pretty clear what happens. If instead you compile enormous epidemiological reports on smokers and reported responses, stratify the results, and present interpolation, there is a lot of wiggle room to say whatever you or your benefactors want to say. If you generate desired conditions for a randomized controlled trial, you can actually prove the opposite of scientific fact WHILE claiming you abided by the gold standard. Scientific fraud and selective data presentation is significantly easier in RCTs than in finite experiments. Try to recall the Nature article above on how 70% of peer-reviewed published research cannot be replicated. Try to guess if that 70% is empirical biologic research or if it is epidemiology. That trend continues to this day. In toxicology and biologic studies, we find that any suspension of aluminum or mercury is unsafe to inject into the body. No matter what type of chemical bond they are in, they cross the blood brain barrier and damage neural cells: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1382668919301875#:~:text=In%20total%2C%20these%20studies%20indicate,of%20concurrent%20detectable%20blood%20mercury https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0013935120306277 The toxicology has no sides. This is irrefutable. It is replicable. Any research facility can conduct the experiment and falsify it. No one has. Likewise, cholesterol cannot generate heart disease. There is no biologic evidence that it ever could. Nothing in biochemistry allows for it. Any research facility could show how cholesterol molecules are generative in cardiovascular disease. None do. There are no sides here. That is the hard science. That is the only science. Until someone comes along with soft science, to present stratified results from meticulously-crafted random controlled trials. They decide on the reporting method. They gather the data. They choose how to contrast groups. They generate the inclusion and exclusion criteria. And then they present an interpretation to create the impression there is a debate or another side. Precisely like when the tobacco companies wanted to invent the appearance of uncertainty or debate, many people today hold up epidemiological results as the superior determinant in scientific causation. In fact, you may get labelled a pejorative simply by asking about mechanism or known biology. In fact, you may find yourself joining in the labelling and tarring and feathering of anyone who asks about empirical science or biologic studies. If we can even take the slightest step back, we can see we have willingly entered total insanity. Imagine awaiting and debating the epidemiology on asbestos and its risks today. If we had not come to a consensus about asbestos and its harm in the 1940s, that would be the case. We would have a whole group of researchers presenting dissenting opinions on the way the RCT data should be interpreted. In fact, it might be considered ignorance to discuss how the microscopic fire-resistant prismatic needles of asbestos destroy human tissue. We might find ourselves ignoring biologic and empirical science about asbestos, only to hold up whatever the industry-funded epidemiology says alone. We have to create a new paradigm. Sadly, in health-related science, we must adopt a painful degree of disapproval, a painful degree of suspicion and distrust. The conflicts of interest run too deep to hand over our trust. If we are to err in a direction, it must be one that opposes powerful organizations. And the more painful behavior within that adoption could be working together with otherwise political or ideological adversaries. It is going to require some serious ego death and eating a lot of humble pie. Even that may be unlikely to solve our crisis, because we need to go the distance and be adamant that epidemiological datasets are not science in the strictest sense. They are tools, but ones subservient to toxicology, biologic studies, empirical experiments, clinical experience, case studies, and reproducible or verifiable facts. There are many medical and scientific thinkers who have already sounded the alarm on the limitations of RCTs. We need to begin listening to them. We need to take up the language of Ellis' and Adams' 1997 paper in the International Journal of Clinical Practice: "The Cult of The Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial." It is not a coincidence that the rise of the cult of the double-blind placebo-controlled trial runs parallel to the worsening of health outcomes. As RCTs have become a religious banner of scientific truth, health outcomes have worsened. As influential people ignore empirical biological facts and known scientific mechanism in favor of epidemiology, the public is getting exactly the wrong messages. We can no longer allow RCTs to command our unquestioning devotion. We can consider them as a very small part of the puzzle - a puzzle whose majority is comprised of biologic studies, toxicology, case studies, empirical experiments, clinical experience. But we MUST NOT keep getting fooled into forgetting the hard science while mesmerized by cherry-picked, fraudulent, or manipulated numbers. We have hit the tipping point with conflicts of interest in human health-related science. We have to be keenly aware of the dangers, between the revolving door, the corporate funding, the interested funding, the advertising juggernaut, and the attempt to replace hard sciences with soft sciences. And we must work together to push back toward a genuine age of science and reason, a genuine democratic effort, a genuine free market. In so doing, may we reclaim common sense itself, our health, our brotherhood of mankind, and our free society. |
Elev8 Wellness
|
LIVE. AWESOME.We offer the highest quality in personal fitness, nutrition, and mindset coaching, helping you achieve your fitness, health, wellness and performance goals no matter the obstacle. With virtual online training and private, in-studio training we make it easier to reach your wellness goals safely.
No more can't. No more not good enough. If you compete in a sport, let your mind no longer hold you back from being the greatest. If you don't, let your mind no longer hold you back from being the best version of you that you can be. Sign-up for a Tour Covid Screen Waiver Elev8 Waiver Become an Elev8 Instructor Space Rental |
6244 lyndale ave. s., minneapolis, mn 55423
|
© 2021 Elev8 Wellness LLC. All Rights Reserved. site map | contribute | SITE BY Sproute Creative

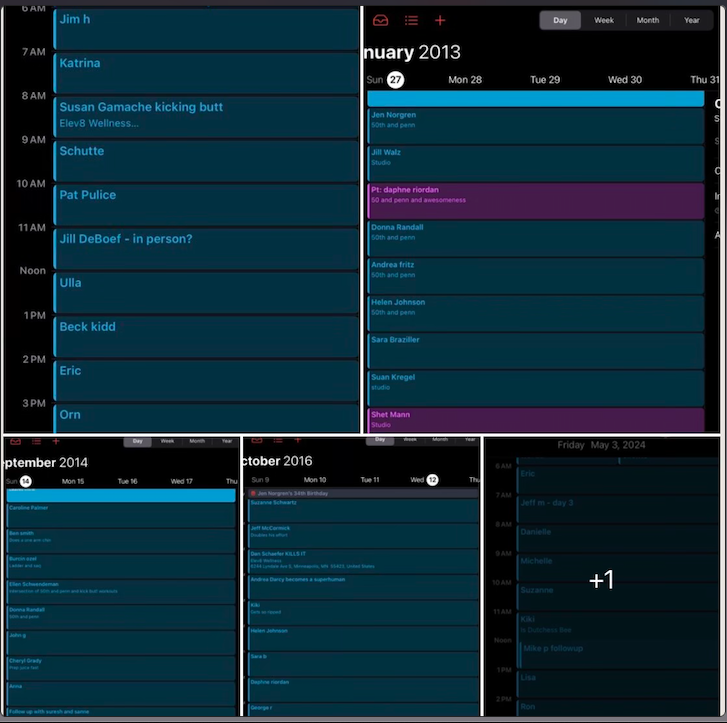




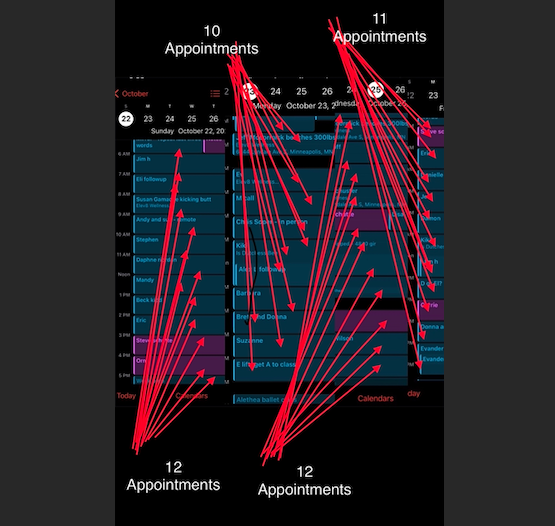



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
